Linkedin Advertising Costs: Models, Benchmarks, and ROI frameworks for B2B Growth
LinkedIn ad pricing sparks heated debates in B2B because the platform often costs more than other paid social channels, yet delivers sharper targeting and higher-quality leads. If you’re balancing budget control with pipeline impact, understanding how LinkedIn charges (and how to bend those costs in your favor) is essential.
This guide demystifies how pricing works (CPC, CPM, CPS) and shows you how to estimate budget, optimize bids, and reduce ad spend without undercutting performance. You’ll get practical calculators, proven benchmarks, and step-by-step frameworks to tighten CAC and accelerate payback.
Who this guide is for
- B2B marketers and growth teams scaling demand gen and lead funnels
- Media buyers and marketing experts seeking tighter control of CPC/CPL
- Teams evaluating whether to engage a digital marketing partner for execution, automation, and attribution
What you’ll learn
- Pricing models and auction dynamics: CPC, CPM, CPS, CPV, and how objectives affect what you pay vs optimize for
- Cost benchmarks: typical CPM, CPC, CPL, and CPS ranges by objective and format (feed, video, Sponsored Messaging)
- Budget math: simple formulas to forecast impressions, clicks, leads, CPL, and CAC
- Bid strategy: when to choose CPC vs CPM vs CPS, manual bids vs max delivery, and pacing controls
- Cost reduction levers: audience refinement, creative upgrades, funnel sequencing, retargeting, and frequency caps
- Measurement and ROI: tracking, attribution, CRM hygiene, and pipeline velocity KPIs
- Execution toolkits: pre-launch and weekly optimization checklists, plus common pitfalls and fast fixes
- Scale support: when a digital marketing partner helps with experimentation, automated lead routing, and CRM integration
Key terms at a glance
- CPC (cost per click), CPM (cost per 1,000 impressions), CPS (cost per send), CPV (cost per view)
- CPL (cost per lead), CAC (customer acquisition cost), CTR (click-through rate), CVR (conversion rate)
- Lead gen forms, Conversation Ads, document ads, retargeting, audience exclusions, bid strategy
Ready to decode what drives your spend and shape campaigns that compound ROI? Let’s start with how LinkedIn’s auction sets prices—and why your objective dictates both bidding options and effective cost.
How LinkedIn advertising costs actually work
LinkedIn advertising costs are set by an auction that weighs your bid alongside predicted engagement and relevance. In practice, a compelling ad with high expected CTR can win placements at a lower effective price than a weak creative with a higher bid. This is why B2B teams see LinkedIn outperform cheaper channels on lead quality when targeting senior, niche buyers. If you understand how the auction values relevance, you can engineer lower costs without sacrificing reach or lead volume.
LinkedIn’s auction system prioritizes delivery to ads that users are most likely to interact with. That probability is modeled from historic behavior, context, and ad quality. Advertisers then choose what to pay for and what to optimize for, which are not always the same. As you plan budgets and pacing, it helps to distinguish billing from optimization and to align your objectives with the right pricing model.
For a deeper look at how relevance and bids interact, see this auction system overview and this comprehensive analysis of LinkedIn ad pricing. Together they explain why ad quality and audience intent often determine the true cost to deliver.
What you pay for vs what you optimize for
LinkedIn lets you pay per click, per impression, or per message send, but you optimize for a downstream goal such as views, clicks, or leads. That split matters because the platform’s objective and optimization signals determine who sees your ad and how often, while your billing model determines what credits your budget.
- Click focused: You pay per click and optimize for traffic or lead form opens. Good when CTR is uncertain or audiences are narrow.
- Impression focused: You pay per 1000 impressions and optimize for reach and engagement. Best when you believe creative will generate strong CTR.
- Message focused: You pay per delivered Sponsored Message or Conversation Ad. Useful for direct outreach at defined accounts or roles.
If you are new to LinkedIn’s levers, scan this practical breakdown of pricing models and this complete guide to cost mechanics in 2025 for model availability by objective.
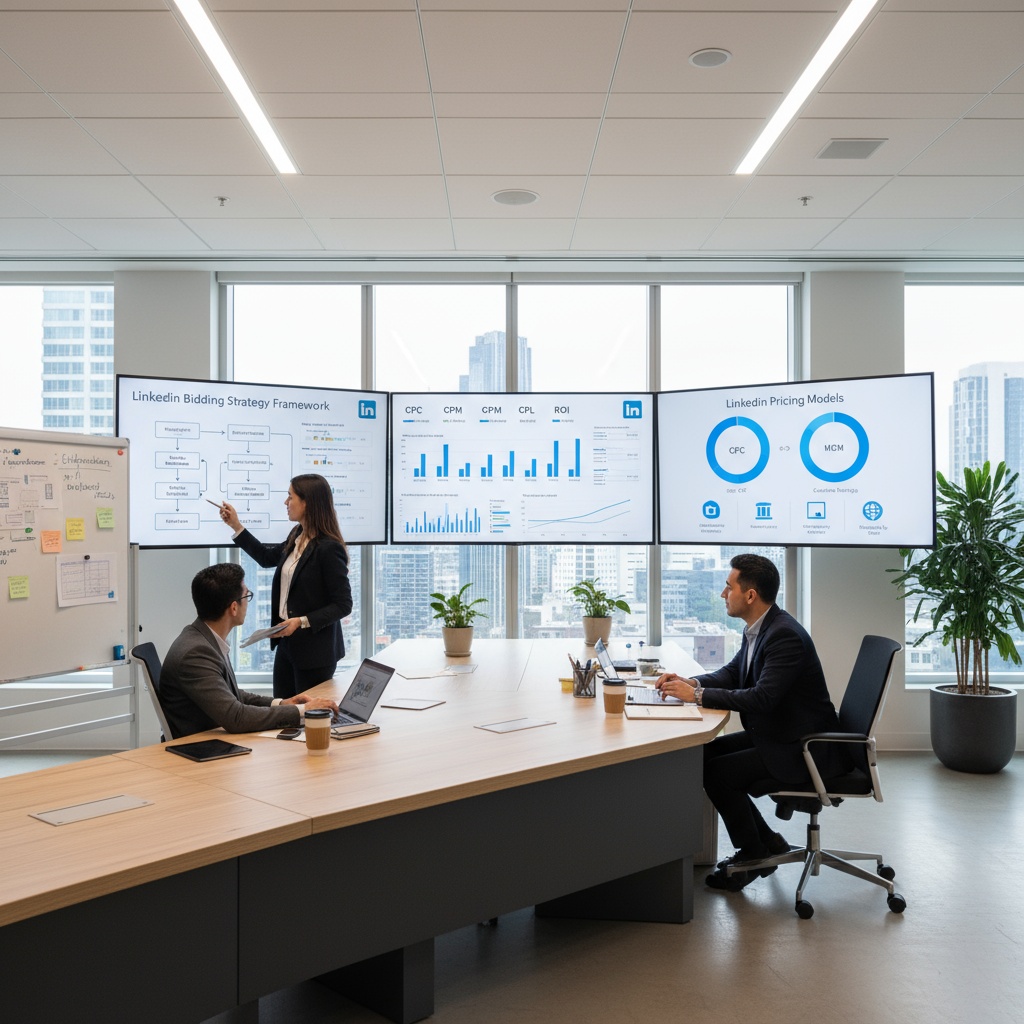
LinkedIn pricing models explained for B2B goals
Below is a quick, comparative view of pricing models and when each tends to shine for B2B teams assessing LinkedIn advertising costs.
| Model | What you pay for | Optimizes best for | Primary strengths | Watchouts |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CPC | Each click | Website traffic, lead forms, niche lead funnels | Control on small audiences, clear pay per engagement | Can throttle reach if CTR is low |
| CPM | Every 1,000 impressions | Awareness and retargeting with high CTR | Efficient scale when ads get strong engagement | Wasteful if creative misses the mark |
| CPS | Each delivered message | Targeted conversations and event invites | Personalization and higher open rates | Frequency controls and audience fatigue |
| CPV | Qualified video views | Video storytelling and education | Low barrier engagement and sequencing | Views do not equal intent without follow up |
| CPL | Calculated outcome metric | Lead gen form efficiency | Useful for benchmarking efficiency | Billing still occurs via CPC or CPM |
If you need a quick primer on campaign setup and budget controls per model, this beginner’s guide and this full guide for B2B planners offer practical checkpoints.
Key drivers of LinkedIn advertising costs you can influence
Several variables make LinkedIn pricier or more efficient than expected. Recognize these early to avoid inflated CPL and CAC.
- Audience size and seniority: Smaller, highly senior, or specialized segments face more competition. Expect higher costs to reach CFOs at mid market and enterprise than general managers. See this full guide on cost drivers for nuance by audience.
- Competitive pressure and seasonality: End of quarter and Q4 tend to raise clearing prices as more advertisers enter the auction. Monitor pacing and cost variance weekly during busy periods.
- Bid strategy and delivery type: Manual bids can control effective CPC and CPM during testing, while maximum delivery helps scale after relevance is proven. Both require enough daily budget to accumulate learning signals. This Bardeen guide summarizes these tradeoffs well.
- Relevance and creative quality: Higher CTR and post click engagement reduce effective costs because the auction rewards ads that perform. Strong offers and clear ICP messaging are often the cheapest efficiency lever you have.
- Campaign structure and data signals: Too many fragmented ad sets slow learning. Proper conversion tracking and the LinkedIn Insights Tag supply the data the system needs to optimize. The iVirtual analysis outlines why signal quality correlates with lower spend for the same outcomes.
Budget estimation framework for LinkedIn ads
Plan your spend with simple math before you launch. You can back into impressions, clicks, and leads from your budget and unit costs, then validate with real data once your campaigns gather traction.
Key formulas:
- Impressions = Budget divided by CPM times 1000
- Clicks = Impressions times CTR
- Effective CPC when bidding CPM = CPM divided by 1000 times CTR
- Leads = Clicks times conversion rate on page or form
- CPL = Spend divided by Leads
- CAC = Spend divided by New Customers
Practical examples:
- Traffic campaign example: Budget 10,000 dollars, modeled CPM 50 dollars, expected CTR 0.6 percent. Impressions 200,000. Clicks 1,200. Effective CPC 8.33 dollars.
- Lead gen form example: If average CPC is 9 dollars and the native form converts at 12 percent, CPL is about 75 dollars. The same 10,000 dollars would produce about 133 leads.
- Message ads example: CPS 0.60 dollars with 10,000 sends. Opens 6,000 at 60 percent open rate. Clicks 300 at 5 percent CTR. If your landing page converts 15 percent, that is 45 leads with an effective CPL of about 133 dollars.
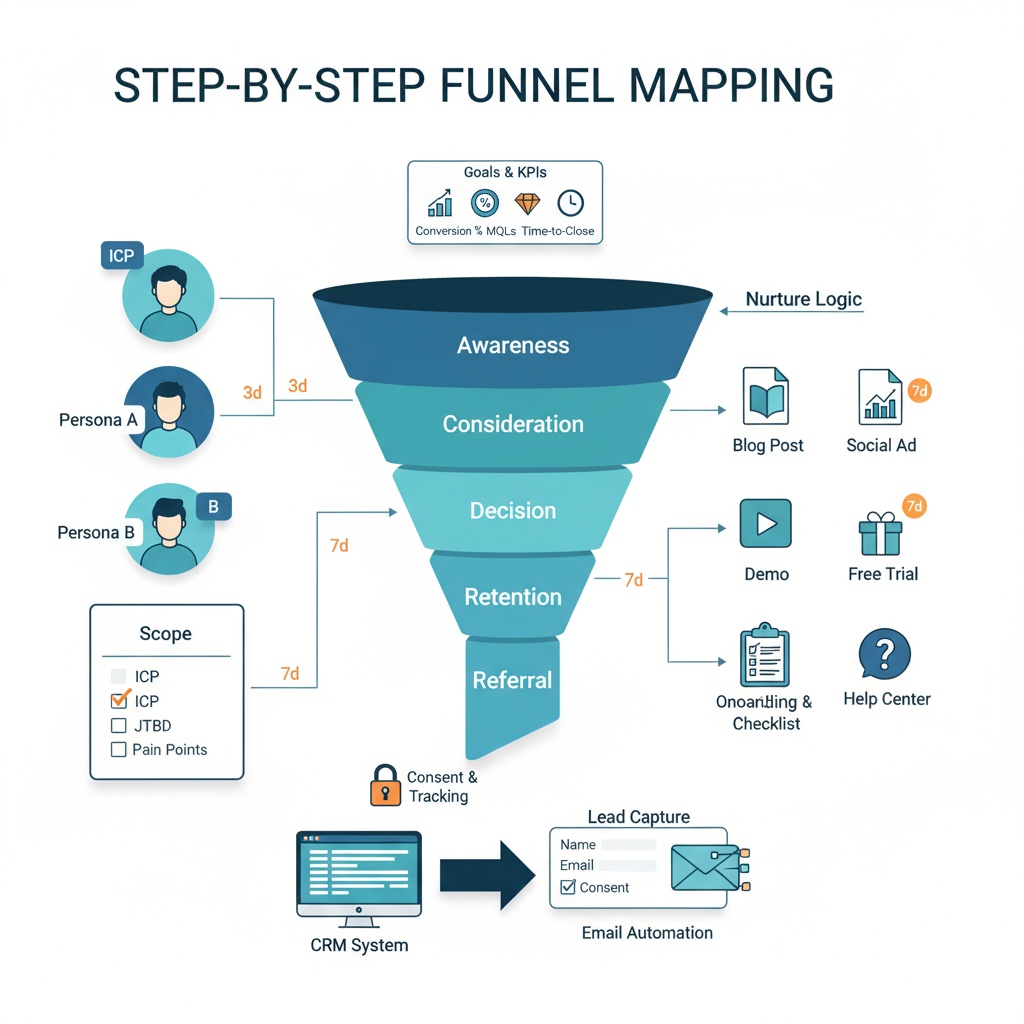
Treat these as directional until you have segment level data. Map them to your actual sales funnel so you can estimate CAC and payback. If your team is formalizing funnel definitions, this guide to sales funnel templates can help you align offer types and handoffs across stages.
Bidding strategy decision guide to control LinkedIn advertising costs
Choosing CPC, CPM, or CPS depends on your goal, your audience, and your confidence in creative performance. Use these rules of thumb to keep spend predictable in the learning phase.
- Pick CPC for niche audiences, bottom funnel intent, or uncertain CTR. You only pay for clicks and can throttle bids as you test.
- Pick CPM when you expect CTR to be strong from retargeting or high resonance creative. You trade per click control for efficient scale on engagement.
- Use CPS for targeted conversations, event invites, or ABM style outreach. Watch frequency and audience fatigue closely to protect sender reputation.
Operational tips:
- Start with manual bids and a daily budget that can accumulate statistically useful data. Graduate to maximum delivery once CTR, CVR, and CPL stabilize. The iVirtual and Bardeen resources outline when to switch.
- Consolidate campaigns to minimize learning fragmentation. Fewer, well structured ad groups outperform many micro tests with thin data.
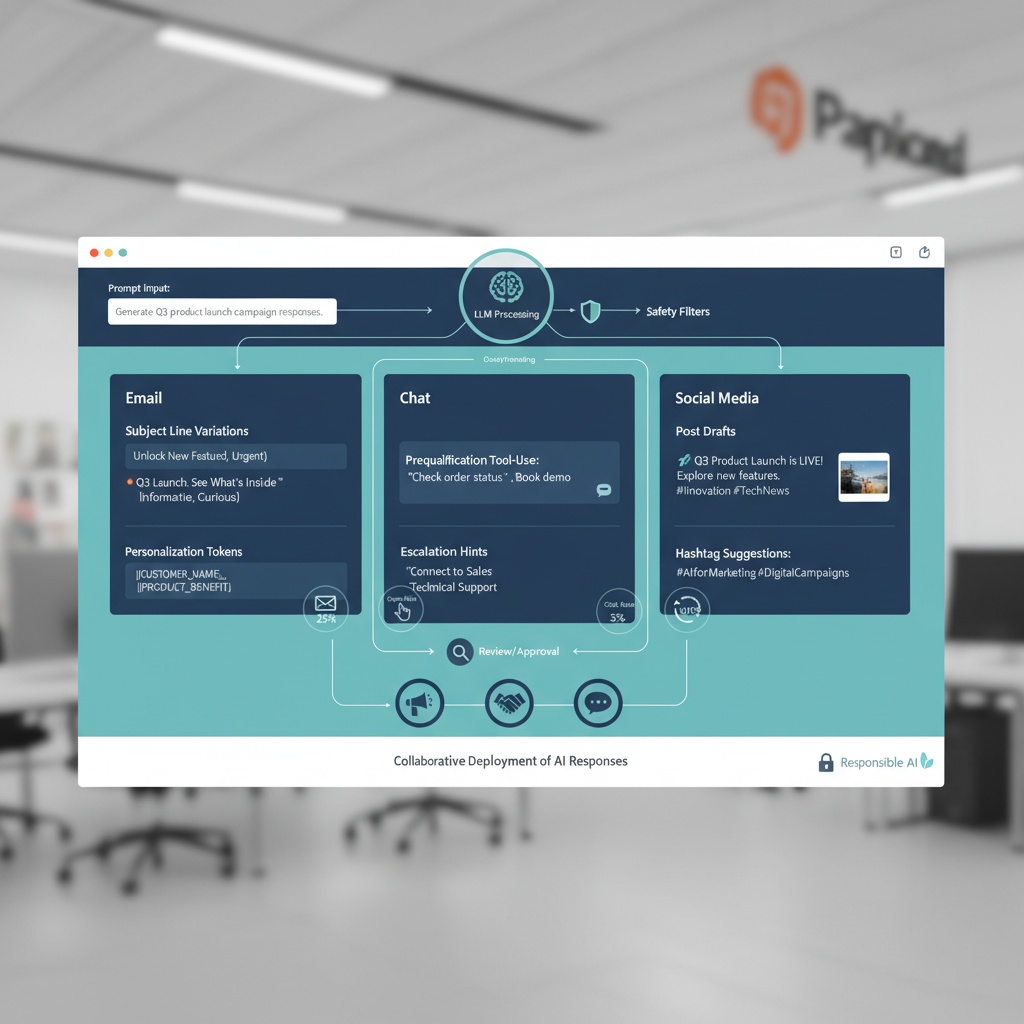
- Cap frequency to avoid waste and set pacing to match your lead handling capacity. If your team plans to use automated lead routing or auto responses, this email response generator guide shows how to keep first touch fast and consistent.
Measurement foundations that protect ROI
Great bidding and creative will not yield efficient results if your measurement stack is weak. Tighten tracking before scaling spend so your optimization signals reflect business value.
- Install and verify the LinkedIn Insights Tag across your site, not just on thank you pages. Configure conversion events for lead form opens, submissions, and down funnel actions.
- Govern UTM parameters and pass first party identifiers to your CRM. This closes the loop between campaigns and opportunity creation.
- Integrate lead forms with your CRM and marketing automation. Route via rules to SDRs, trigger alerting, and set SLAs for first response. Automated lead workflows keep follow up inside a five minute window.
- Align definitions for MQL and SQL with sales. Consistent scoring prevents spend on leads that never convert. If you need help with channel tradeoffs in the broader mix, this comparison of SEO vs PPC can sharpen planning assumptions.
- Track pipeline, win rate, and payback for each campaign. Layer multi touch attribution in your CRM to value both prospecting and retargeting influences. This comprehensive analysis and this cost overview for B2B advertisers provide helpful KPI baselines and modeling ideas.
Where this sets you up for cost benchmarks and optimization levers
You now have a working model for how the auction values relevance, how pricing models interact with objectives, and how to forecast impressions, clicks, and leads from any budget.
In the next section we will quantify typical CPM, CPC, CPV, CPS, and CPL benchmarks by objective, then translate those figures into a pragmatic plan for reducing spend without undermining ROI using audience design, creative offers, funnel sequencing, and smarter bidding supported by clean tracking and CRM data.
From Benchmarks to Unit Economics: Turn CPM and CPC into Target CPL and CAC
Benchmarks only matter if they roll up to profitable unit economics. Translate your expected CPM and CPC into a target cost per lead and customer acquisition cost that your finance team will accept.
- Start with revenue math: Average contract value, gross margin, target payback period.
- Map funnel conversion rates: Impression to click, click to lead, lead to MQL, MQL to SQL, SQL to closed-won.
- Derive guardrails: Target CPL equals CAC target multiplied by win rate and SQL rate, then divided by the conversion steps above. This sets the maximum you can afford before a single dollar is spent.
Example for a B2B SaaS selling at 25k average contract value with 75 percent margin, 6 month payback, 18 percent win rate from SQL, 45 percent MQL to SQL, and 30 percent form conversion. The CAC ceiling is roughly 9,375. The target CPL is near 250 when you factor typical stage rates. If your modeled CPC and CVR from the earlier benchmarks yield a projected CPL above that 250, fix creative and audience first, not spend more on reach.
Use this approach to compare linkedin advertising costs with other channels. If LinkedIn’s projected CAC is closer to your ceiling than paid search, LinkedIn should carry a lower budget share until conversion efficiency improves.
Industry Modeling: How Cost Structure Shifts by Vertical
Costs vary with seniority, niche density, and offer type. Model scenarios, not averages.
- Enterprise SaaS selling to IT leaders: Expect lower CTR due to heavy decision committees. CPC may be higher, but webinar offers drive better form conversion and pipeline quality. Prioritize document ads and event campaigns to sustain relevance while controlling CPM.
- Professional services targeting CFOs: Smaller reachable audience, higher competition. Message ads may produce premium CPS, yet calendar conversion can offset ad costs. Sequence case study video views to build familiarity before direct consult offers.
- Manufacturing and industrial: Broader role-based targeting can lower CPC, but niche technical content caps CTR. Use thought leadership and calculators to boost engagement. Retarget to lead gen forms once engagement pools are large enough.
Cross-reference scenario planning with the updated overview from The B2B House and the comprehensive analysis by iVirtual to validate feasibility.
Budget Architecture: Pacing, Frequency, and Learning Plans
Link budget to a learning agenda. Spend should fund answers to precise questions.
- Allocate to experiments, not only channels. Example split: 60 percent proven programs, 30 percent structured tests, 10 percent wildcards.
- Cap effective frequency: Many B2B advertisers overspend at frequency above 8 per month, which decays marginal returns. Evaluate brand recall and lead quality at incremental frequency steps to identify saturation points.
- Stabilize learning with sufficient volume. Avoid slicing micro audiences into too many campaigns. Prioritize one audience per funnel stage to accelerate delivery.
- Time the market: Q4 and end-of-quarter spikes inflate auction pressure. Shift upper funnel to earlier months and reserve MOFU retargeting for tighter windows when competition surges.
When your CTR is consistently above 1 percent on certain ad sets, test CPM buying to scale at a lower effective CPC. If CTR is volatile, revert to CPC until creative reliability improves. For deeper nuance on auctions and delivery, review Octopus CRM’s auction overview and Bardeen’s full guide.
Offer and Creative System: A Testing Matrix That Reduces Costs
Creative controls effective CPC and CPL more than small bid tweaks. Build an offer system that compounds learning.
- Three-track matrix: education, proof, and action. Education includes benchmark reports, primers, and frameworks. Proof highlights case studies, ROI calculators, and customer clips. Action prioritizes trials, demos, or pricing.
- Consistency across formats: Repurpose the same thesis into single image, document ad, short video, and message templates so you can isolate how format shifts cost and engagement rather than changing the message.
- Message angle sprints: Run two-week sprints around a single pain point with at least two creative variants. Keep copy direct and mobile-first. Add specificity with industry stats from credible sources like WebFX’s pricing insights to frame expectations.
- Scale what converts: Once an angle yields 2x account average CTR and 1.5x form conversion, port it into conversation ads for targeted outreach and into email nurture. The same thesis should power your nurture sequences and retargeting.
Tie this to your broader nurture plan with the guidance from newsletter and email marketing and deepen funnel orchestration using the sales funnel templates resource.

Data Integrity and Signal Quality: The Hidden Lever Behind Cost
The auction rewards predicted engagement and conversion. Signal quality determines whether the algorithm sees your account as low risk.
- Instrumentation: Install the LinkedIn Insight Tag, enable the Conversions API, and push offline conversions for opportunities and revenue. Deduplicate with UTMs to prevent double counting across paid social and email.
- Event taxonomy: Standardize event names, values, and attribution rules. Use primary conversion for the stage you are funding and track micro-events for optimization hints.
- Lead hygiene: Validate business emails, standardize job seniority fields, and enforce CRM required fields that map cleanly back to the platform. Dirty data inflates CPL and hides pipeline inefficiency.
- Speed to lead: Route LinkedIn Lead Gen Forms into your CRM with an automated lead workflow, push Slack alerts to owners, and set a five minute SLA for first contact. Use an email response generator workflow to ensure consistent and timely outreach.
For deeper conversion modeling and tracking mechanics, Bardeen’s full guide and iVirtual’s comprehensive analysis provide step-by-step configurations.
Bidding and Delivery Tactics: Practical Moves That Shift Efficiency
Execution details move the needle more than high-level strategy.
- Manual control first, scale later: Launch with manual bids to find a clearing price. Once CTR and conversion stabilize, switch to maximum delivery to capture incremental volume without manual babysitting.
- Clean splits to avoid self-competition: Separate campaigns by objective and cold versus warm audiences. Do not stack retargeting and prospecting in the same ad set if you want clean readouts.
- CPS and conversation ads with guardrails: Build audience lists of engaged users for message sends to protect CPS from cold wastage. Cap sends per user within a quarter to preserve goodwill.
- Dayparting tests: Some industries show stronger intent during business hours. If you see noisy overnight spend with weak conversion, test dayparting and compare effective CPC and CPL.
- Format rotation: Rotate document ads, short video, and single image to defend CTR over time. Fatigue raises costs slowly and silently.
Cleverly’s pricing insights and Quickads’ beginner’s guide add tactical nuances on budget capping and spend pacing that complement these moves.
When LinkedIn Is Not the Cheapest Path and How to Blend Channels
LinkedIn will not always be the dominant channel for every audience or offer. Senior financial roles, hyper-local targets, or low ACV products can suffer from thin engagement and tough win rates.
If your modeled CAC from LinkedIn exceeds ceiling thresholds while paid search remains efficient, shift budget toward high intent queries and use LinkedIn to prime demand with cost-controlled video and document ads.
See the SEO vs PPC comparison for a practical view of cost, timeline, and ROI tradeoffs, then allocate budgets based on intent density and sales cycle length rather than platform preference.
Building a Conversion-Centric Lead Funnel With Automation
A single-platform plan rarely carries growth. Use LinkedIn to generate intent, then convert with orchestrated nurture.
- TOFU: Promote ungated insights and short video that build a retargeting pool. Set frequency limits and collect engagement audiences.
- MOFU: Gated assets and events that qualify interest. Align topics with pipeline stages. Integrate automated lead routing and deduplication to keep contact ownership clear.
- BOFU: Trials and demos for hot audiences only. Use conversation ads sparingly for buyers who engaged with two or more MOFU signals.
Connect this motion to your CRM and build automated lead tasks, sequences, and scoring. The sales funnel templates guide helps map handoffs, while the email response generator guide shows how to scale considerate follow-ups without sacrificing personalization.
Deciding When to Bring in a Digital Marketing Partner
If experimentation stalls, or your team cannot keep up with creative rotation, consider a digital marketing partner. Look for marketing experts who provide weekly test plans, audience research beyond default titles, and CRM integration audits.
Evaluate them on pre-post lift in SQL rate, not just CPL. Ask for case studies where they rebuilt lead funnels, tightened routing, and delivered automated lead handling that cut response time to minutes. External frameworks from iVirtual, The B2B House, and WebFX offer helpful validation criteria during vendor selection.
Advanced Playbook: Concrete Actions for the Next 30 Days
- Define unit economics: set target CPL and CAC by product line and region.
- Assemble your first creative matrix with three angles and three formats.
- Launch controlled manual bids, document clearing prices, then test max delivery on winners.
- Build a clean retargeting pool with 90-day video viewers and document engagers.
- Enable the Conversions API, configure offline conversions, and test deduped UTM tracking.
- Implement automated lead routing, assign owners, and enforce a five minute SLA.
- Compare cost per opportunity across LinkedIn, paid search, and partner syndication. Shift budget each week based on pipeline yield.
- Align nurture sequences with your offers, and improve open rates with strategies from newsletter and email marketing.
Conclusion
Ultimately, winning on LinkedIn comes down to disciplined control of pricing, precise targeting, and creative that earns attention. When you understand linkedin advertising costs, the auction mechanics, and which bid model maps to your objective, you stop guessing and start engineering outcomes. The evidence shows that while rates run higher than other channels, the platform’s reach into senior, high-intent audiences delivers lead quality that pays back.
Budget with intent, not hope. Use the formulas to forecast reach, clicks, and leads; apply the benchmarks as guardrails; and move from manual bids to scale only after you’ve proven relevance and conversion. Consolidate your structure for faster learning, cap frequency to manage waste, and let data—not hunches—determine pacing and spend.
Protect ROI with rigor. Tighten audiences and exclusions, refresh creative on a cadence, and sequence TOFU, MOFU, and BOFU offers to match buyer readiness. Install tracking, pass clean conversion signals to your CRM, and enforce speed to first touch with automated lead routing. Align on MQL/SQL definitions and SLAs so marketing and sales move in lockstep.
Measure what matters and act decisively. Track CTR, CVR, CPL, and CAC by stage, build retargeting pools, and apply clear kill rules to underperformers. Lead funnels that progress from education to conversion, backed by accurate attribution, compound efficiency over time.
In conclusion, the path is clear: apply the frameworks, calculators, and checklists, launch a focused pilot with explicit objectives and budgets, automate the handoff to revenue systems, and scale what proves out. If you’re managing complex rollouts or need deeper muscle, engage a digital marketing partner and seasoned marketing experts to accelerate audience research, testing velocity, and full-funnel design. Act now, lock in your learning loops, and turn spend into a predictable growth engine.
Frequently Asked Questions
Plan for a 2–4 week test per objective with enough spend to reach statistically useful volume. Back into budget from your target CPL: if you need a $150 CPL and want 60 leads to learn, allocate about $9,000. For traffic learning, aim for 1,000–2,000 clicks (e.g., at an $8–$12 CPC, budget $8,000–$24,000 across a month). Keep campaigns consolidated: 1–2 campaigns per objective with 2–4 ads each, and avoid slicing audiences too thin so the algorithm learns faster.
Use CPC when CTR is uncertain or your audience is narrow—this gives cost control for down-funnel actions. Choose CPM once creative is proven and you expect CTR >1% (awareness, retargeting, high-engagement offers). Opt for CPS (Sponsored Messaging) for targeted outreach like event invites or ABM, especially when you can personalize by job title/seniority and align the message to a timely hook.
High CPL often traces to misaligned offers, overly narrow audiences, or low CTR creatives. Fixes include: upgrade the offer (calculators, benchmarks, templates), simplify lead form fields, broaden targeting by skills/roles while excluding competitors/employees, and rotate creatives every 2–3 weeks. Cap frequency to avoid fatigue (aim for 2–6), retarget engaged visitors, and start with manual bids to find an efficient clearing price before switching to max delivery. Protect lead quality by aligning MQL/SQL definitions and scoring in your CRM.
For cold prospecting, target 50k–300k members per ad set; for retargeting, 5k–50k works well. Keep structure simple: 1–2 campaigns per objective, 2–4 ads per ad set, and avoid duplicating tiny segments that dilute learning. Layer skills + seniority + industry for relevance and use exclusions (customers, employees, competitors) to improve efficiency. This balance sustains delivery while maintaining relevance.
Use a simple chain: Budget → CPM/CPC → CTR → CVR. Example: $10,000 at a $50 CPM = 200,000 impressions; at 0.6% CTR, that’s 1,200 clicks; at 12% CVR, expect 144 leads; CPL ≈ $69. For CPM buys, estimate effective CPC as CPM / (1000 × CTR). Map scenarios (base, best, worst) by flexing CTR and CVR to set realistic expectations and guardrails.
They can be—if your CAC:LTV math works and you focus on warm traffic. Start with retargeting and lookalike/matched audiences, test lead gen forms to reduce drop-off, and run short, value-led offers that convert quickly. If your realistic CPL is $120–$250, ensure downstream SQL rate and win rate produce an acceptable CAC for your price point. For very low ACV, consider LinkedIn primarily for influence and retargeting, with search and email nurturing doing more of the heavy lifting.
Build a sequenced lead funnel: TOFU (ungated video, document ads) to drive reach, MOFU (webinars, calculators) to generate leads, and BOFU (demos, trials) for conversions. A common split is 60/30/10 across TOFU/MOFU/BOFU, with time windows (e.g., 30/60/90 days) for retargeting. Use document ads and strong CTAs to uplift CTR, and ensure automated lead capture flows into your CRM for timely follow-up.
Connect LinkedIn Lead Gen Forms to your CRM/marketing automation and trigger instant alerts to sales (Slack/Email/SMS). Enforce an SLA of <5 minutes first response—speed dramatically increases connect and qualification rates. Add enrichment and lead scoring to prioritize, and create fallback queues so no automated lead is missed outside business hours.
Monitor CTR, CPC/CPL, and frequency. As directional guides: CTR ≥0.6–1.0% (feed ads), CPC $5–$15 for most industries, Lead Gen Form CVR 10–20%, and frequency 2–6 depending on audience size. Apply kill rules (e.g., pause ads 30% worse than median CPL after $500–$1,000 spend) and reallocate to top quartile performers. Always validate performance in CRM with pipeline and win rate.
Bring in a digital marketing partner when you face scaling challenges, complex attribution, or limited creative/ops capacity. The right marketing experts will refine ICP targeting, craft conversion-centric offers, implement experimentation roadmaps, build automated lead flows, and model ROI from click to revenue. Evaluate partners on relevant case studies, transparent KPIs/SLAs, and proven lead funnel architecture that ties ad spend to pipeline.