Yoast SEO training: a step-by-step WordPress blueprint for setup, on-page optimization, schema, sitemaps, and Google Search Console
If you run WordPress and want predictable, repeatable SEO wins, this guide is your playbook. We’ll walk you through a structured, hands-on process to configure the Yoast plugin, optimize content, and align your site with Google’s best practices.
Built as a search engine optimization tutorial for beginners, it reads like a compact technical SEO course. Expect practical checklists, smart defaults, and real workflows that move your site from invisible to indexable—and from indexable to clickable.
Whether you’re launching your first blog or tuning a mature site, you’ll learn how to turn Yoast’s features into a coherent SEO system: titles and meta, schema markup, XML sitemaps, indexation controls, and Google Search Console monitoring.
What you’ll learn in this search engine optimization tutorial for beginners
- Install, activate, and run Yoast’s First-time Configuration the right way
- Set global features: SEO analysis, readability checks, XML sitemaps, breadcrumbs, and webmaster verification
- Craft search appearance templates: titles, meta descriptions, and separators for posts, pages, and custom post types
- Control taxonomies and archives (noindex thin tags/date archives to prevent index bloat)
- On-page workflow: focus keyphrase selection, H1 and slug alignment, meta descriptions, alt text, internal/external links
- Readability and content structure: subheadings, transition words, passive voice, sentence length
- Schema and structured data: global entity setup, per-post schema types, FAQ/How-to blocks, rich results validation
- XML sitemaps: discover, prune, and avoid duplicates; understand noindex vs exclude
- Meta and robots controls: index/follow, canonical URLs, Open Graph and Twitter Cards
- Google Search Console training: verify, submit sitemaps, inspect URLs, read Coverage and Enhancements, fix indexing and schema issues
- Technical SEO course essentials: clean permalinks, robots.txt/.htaccess awareness, staging and conflict checks, performance and image optimization
- Checklists, templates, and mini case studies to operationalize your SEO tutorials learning
Who this guide is for
- WordPress site owners, bloggers, and editors new to SEO
- Marketers who want a tidy, scalable workflow using the Yoast plugin
- Teams seeking a reliable foundation before advanced technical SEO
Before you start: prerequisites
- WordPress admin access and an up-to-date WordPress/PHP stack
- Only one SEO plugin active (Yoast), with a staging site strongly recommended
- Basic familiarity with posts, pages, categories, and media in WordPress
How this technical SEO course is structured
- Setup and first-time configuration
- Global settings and search appearance
- On-page optimization workflow
- Schema, sitemaps, and meta/robots governance
- Deep-dive google search console training
- Checklists, pitfalls, and advanced tips for multilingual sites, redirects, and internal linking
Ready to put Yoast to work? We’ll begin with installation and the First-time Configuration wizard, then build out your search appearance and sitewide foundations.
Start your Yoast SEO training: prerequisites, safety, and the right mindset
Before you touch settings, confirm your site is ready for a technical SEO course style workflow. You need WordPress admin access, recent PHP and WordPress versions, and ideally a staging site to test changes without risking production. Conflicts between SEO plugins are the most common early failure, so plan to run only one SEO plugin at a time.
Yoast will centralize titles, meta tags, sitemaps, and schema. That means your theme and other plugins should not inject their own SEO outputs. If they do, you will see duplicated titles and robots tags in the HTML. Resolve this now rather than later by disabling overlapping SEO features in those tools.
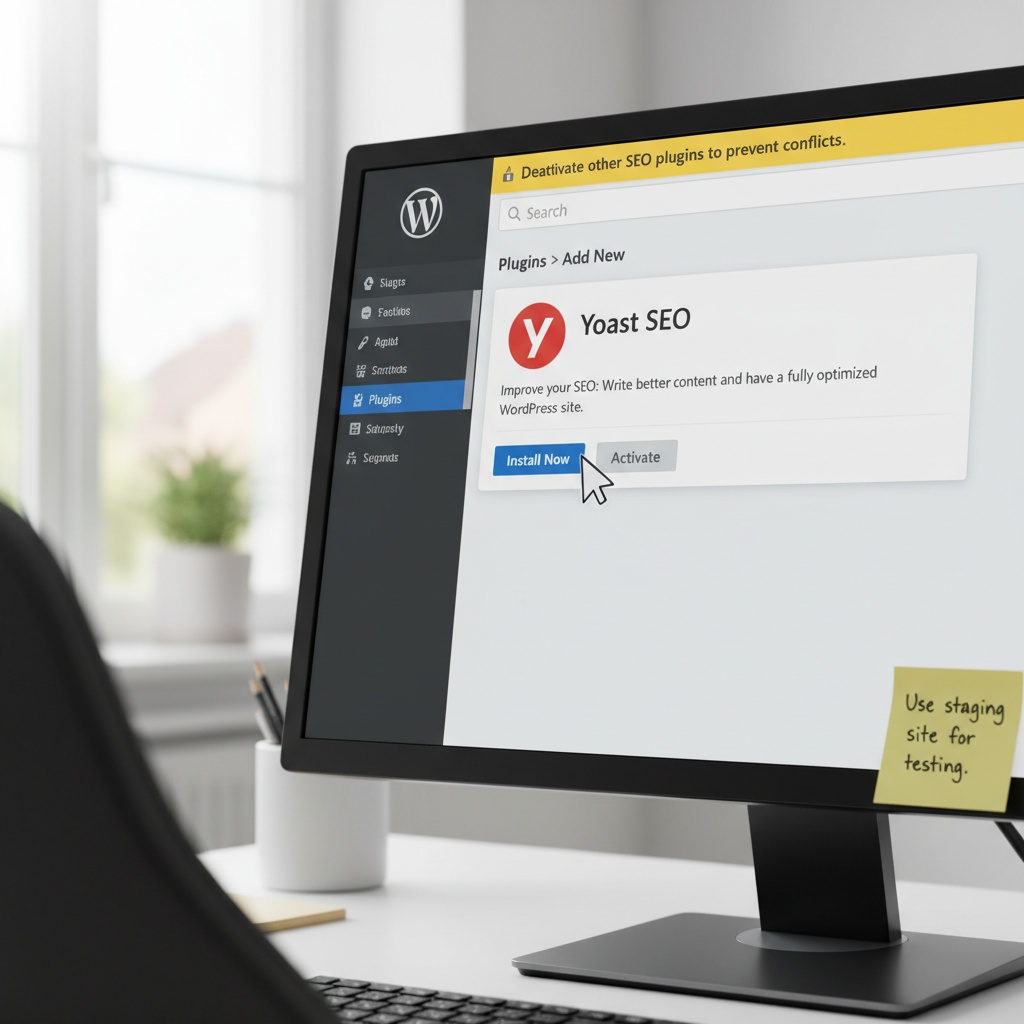
Install and activate the Yoast plugin correctly
You can install Yoast from your WordPress dashboard in under a minute, and this exact sequence matters. Navigate to Plugins, choose Add New, search for “Yoast SEO,” then select Install Now and Activate. The same process is outlined in the Semrush guide to Yoast SEO and the Kinsta complete tutorial, which are reliable references if you hit an unusual theme or hosting configuration.
Quick checklist for a clean install:
- Update WordPress and PHP to supported versions
- Confirm only one SEO plugin is enabled
- Prefer a staging site for initial configuration and testing
- Keep a rollback plan through backups or host snapshots
If you are a visual learner, the YouTube beginner tutorials are excellent companions while you work. Try the Complete Yoast SEO Tutorial For Beginners 2025 and the Yoast SEO Tutorial 2025 for an at-your-desk walkthrough.
Global Yoast settings that form your technical SEO course baseline
Treat this section as your system defaults. These toggles and templates influence every page and will shape how search engines interpret your site.
Core features to enable for analysis and automation
Turn on SEO analysis, Readability analysis, and XML sitemaps. These give you scoring, inline guidance, and automatically generated sitemaps without code. Consider enabling Inclusive language analysis if tone matters to your brand. Breadcrumbs can be enabled if your theme supports them and you want improved navigation trails in search results. The Kinsta tutorial on Yoast configuration explains each feature’s function and when to enable it.
Security settings that prevent accidental damage
Disallow authors and editors from changing advanced meta on published posts. This prevents a well-meaning content update from flipping a page to noindex or altering a canonical URL. You keep centralized control while still empowering content teams to optimize titles and descriptions.
Webmaster tools fields to prepare for Google Search Console training
Yoast exposes fields for verification codes from major search engines. You will use these fields during your upcoming google search console training sequence. Keep them handy and avoid installing separate verification plugins that add bloat.
Search appearance configuration that protects index quality
Search appearance impacts how your titles, descriptions, and archives are presented. Well-chosen templates and index rules prevent index bloat and keep your results readable.
Title and meta templates that scale cleanly
Use consistent variables to keep titles readable and branded. A pragmatic default is:
- Title template for posts and pages: %%title%% %%sep%% %%sitename%%
- Meta description: a curated sentence crafted per page rather than a generic template
These patterns are described in the Kinsta complete tutorial and reinforced in the Yoast beginner’s guide. The point is consistency and clarity, not keyword stuffing.
Taxonomies and archive hygiene
Most sites should set tags and date archives to noindex. Category archives can be indexed if they are curated and valuable. Thin archives dilute crawl budget and confuse users. Turning off low-value archives now prevents months of cleanup later.
Breadcrumbs and RSS signals
Enable breadcrumbs if your theme supports them. They enhance navigation for users and provide structured paths for search engines. In RSS settings, add attribution and a link back to the original post. Include UTM parameters to help you detect scrapers and attribute traffic correctly.
On-page optimization workflow with Yoast’s analysis
Yoast’s content analysis gives beginner-friendly, step-by-step feedback while still useful for experienced editors. Use it to standardize your editorial process across teams.
Pick a focus keyphrase and align with intent
For each page, choose a focus keyphrase that matches search intent. Use light research in tools like the Semrush guide to Yoast SEO or your preferred keyword tool. The keyphrase guides the analysis; it does not replace editorial judgment.
Optimize title, slug, and meta description
Write a human-first title, a readable slug, and a concise meta description. Place the keyphrase early, but ensure the copy would earn a click from a real reader. Treat the Yoast snippet preview as a mini ad.
Follow the SEO analysis without gaming it
Aim to satisfy the checks for keyphrase placement in the H1, the first paragraph, subheadings, image ALT text, and internal links. Do not force awkward phrasing to turn every indicator green. The YouTube beginner tutorials show sensible examples of balancing green bullets with natural language.
Improve readability for real users
Shorten long sentences, add subheadings for scannability, and increase transition word usage where appropriate. Readability scores correlate with engagement, which supports better outcomes even if it is not a direct ranking factor.
Mini case: An ecommerce blog rewrote meta descriptions for 25 guides using this workflow. CTR improved by 12 to 18 percent on posts that moved from vague copy to clear problem-solution descriptions. Rankings were unchanged, but traffic rose instantly because more searchers chose their result.
For deeper content techniques, see our SEO copywriting training that pairs templates with live editing exercises.
Schema and structured data with Yoast for beginners
Yoast outputs clean schema by default. Site-wide, it declares your entity as a Person or Organization and assigns logical types such as WebPage or Article at the page level. This creates a graph that search engines can interpret without you touching code.
Enhance with per-post schema and blocks
For how-to guides and FAQs, use the Yoast FAQ and How-to blocks in the block editor. These produce structured data eligible for rich results. On product or custom post types, confirm the default type is appropriate and override it when needed.
Validate and observe
Test your pages with Google’s Rich Results Test to confirm there are no syntax errors. In Search Console, the Enhancements report will later show coverage and eligibility. You will connect these dots when you reach the hands-on google search console training section.
XML sitemaps management in Yoast
Your sitemap index lives at /sitemap_index.xml when XML sitemaps are enabled. This index references sub-sitemaps for posts, pages, categories, and other content types.
Control inclusions without harming discoverability
Decide which post types and taxonomies deserve inclusion. Excluding thin or private content reduces noise. Understand the difference between noindex and exclude to avoid unexpected outcomes.
Extended comparison of common controls:
| Control | What it does | When to use | Effect on sitemap | Effect on indexing |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Noindex | Adds a robots meta noindex on the page | Thin pages that must exist for users | Usually remains listed | Page is crawled but not indexed |
| Exclude from sitemap | Removes the URL from the XML sitemap | Auto-generated, low-value archives or experimental content | Not listed | Discoverability reduced unless linked elsewhere |
| Disable archive | Turns off an entire archive type | Tag archives on large blogs with no strategy | Entire archive omitted | URLs return 404 or redirect when configured |
Avoid duplicate sitemap providers. If your theme or a caching plugin outputs its own sitemap, turn that off and let Yoast be the single source of truth.
Meta tags, robots controls, and canonical management
Page-level controls in the Yoast meta box are your safety valves. Use them to shape crawling, indexing, and consolidation of signals.
- Index or noindex: Keep critical pages indexable. Noindex thin archives, login pages, and thank-you pages
- Follow or nofollow: Leave as follow unless you have a strong reason to withhold link equity
- Canonical URL: Consolidate variants such as UTM parameters, print versions, or paginated series into a single canonical
For social previews, set custom Open Graph and Twitter Card fields. This improves sharing consistency and prevents poorly cropped images or truncated titles. If you need a refresher, the WordPress SEO tutorial from Yoast and the Kinsta complete tutorial cover common pitfalls with social metadata.
Technical SEO course essentials to verify now
Before you proceed, confirm baseline platform settings that affect every optimization you make.
- Disable “Discourage search engines from indexing this site” in WordPress Reading settings
- Use clean permalinks such as /%postname%/ for stable, readable URLs
- Ensure robots.txt and .htaccess exist and do not block critical resources like CSS and JS
- Optimize images and performance to reduce bloat that harms Core Web Vitals
If you are building a long-term learning path, our free SEO training roadmap explains how to layer practice tasks and checkpoints across weeks. For data-driven workflows, explore machine learning in SEO to streamline keyword research and content optimization.
Checklists to keep your Yoast SEO training on track
One-time setup checklist:
- Update WordPress and PHP
- Install and activate Yoast
- Remove other SEO plugins or disable overlapping features
- Enable core features and review security settings
- Sketch your title templates and archive index rules
Per-post on-page optimization checklist:
- Define a focus keyphrase aligned to search intent
- Write a clear title, readable slug, and compelling meta description
- Use the keyphrase in H1, intro, subheadings, and image ALT where natural
- Add internal links to cornerstone content and relevant resources
- Confirm schema type and enhance with FAQ or How-to blocks when suitable
GSC monitoring checklist you will use after connection:
- Watch Indexing Coverage for unexpected noindex or blocked pages
- Review Enhancements for schema eligibility and errors
- Inspect low-impression URLs to diagnose canonical or duplication issues
Troubleshooting checklist:
- Audit for duplicate titles or meta descriptions
- Noindex thin archives and redundant tag pages
- Resolve 404s and implement redirects for moved content
- Check theme or plugin conflicts that overwrite Yoast titles or robots tags
Common pitfalls and best-practice fixes
- Indexing low-value taxonomy pages. Set tags and date archives to noindex unless you curate them
- Conflicting metadata. Let Yoast own titles and meta, and disable competing outputs
- Multiple sitemaps. Remove duplicates and submit one clean index when you connect Search Console
- Accidental noindex. Lock down advanced meta for authors and review high-value page settings regularly
Advanced tips for complex WordPress sites
Multilingual sites need clean hreflang and separate sitemaps per language. Validate that each language has its own index in the sitemap and that canonicals point to the correct language version. For redirects, Yoast Premium helps with simple 301s, while dedicated tools handle complex patterns. Reinforce internal linking by designating cornerstone content and linking to it from related posts, category pages, and navigation. For structured learning beyond this search engine optimization tutorial for beginners, the Yoast SEO academy and the Yoast beginner’s guide are reliable resources.
Where this search engine optimization tutorial for beginners goes next
With installation complete, your features aligned, and your on-page workflow defined, you are ready to configure the site in Yoast’s First-time Configuration and then connect reporting. In Part 2, you will configure site representation, refine indexing preferences for post types and taxonomies, enable advanced controls, and complete the hands-on verification and sitemap submission in Search Console so you can monitor coverage, enhancements, and performance over time.
Beyond the Wizard: Decisions That Shape Your Entire SEO Footprint
Treat the First‑time Configuration in Yoast as a strategy step, not a checkbox. Person vs Organization is not cosmetic. It the cornerstone of your entity in Google’s knowledge systems. Choose Organization if the brand is the primary entity and ensure your logo is a square image that still looks distinctive at small sizes. Use consistent social profiles as SameAs identifiers. If a founder is central to the brand, keep Organization in Yoast, then reflect the person prominently in on‑site schema via author pages and About content so Google can connect both entities. For solo creators who are the brand, Person can be correct, but confirm that on‑site branding, bylines, and profile data support that choice.
Indexing preferences should align with a clear information architecture. A practical rule: index only templates that (1) capture search demand, (2) present unique value, and (3) have scalable content quality. For many sites, that means indexing posts/pages and curated category archives while setting tag archives to noindex. For ecommerce, index product and carefully curated category pages, noindex filter facets and internal search results. For SaaS documentation, index evergreen guides, noindex auto‑generated release notes and duplicate versioned docs unless canonicalized. In news publishing, keep author archives only if authors are recognized entities with dedicated profile content; otherwise noindex to reduce index bloat.
When you enable advanced settings, align permissions with governance. Limit who can change indexation or canonical settings. Adopt a change log that records what was toggled, by whom, and why. This lightweight workflow prevents accidental sitewide noindex and helps during audits.
For more nuance on these decisions, the Semrush guide to the plugin and the Kinsta tutorial both offer setup perspectives worth comparing. You can also examine the Yoast academy overview for schema and search appearance patterns.
A decision checklist you can adopt immediately
- Choose Organization unless you are a personal brand with strong author‑entity signals
- Add social profiles that you actively maintain for consistent identity mapping
- Index only templates with intent‑driven content and a plan to maintain quality
- Noindex thin archives, utility pages, and duplicates, then remove them from sitemaps if they have no purpose in discovery
- Document permission boundaries and keep a change log tied to Search Console annotations
Google Search Console Training: From Verification to Insight Loops
Verification through the HTML tag in Yoast is the on‑ramp. The real work begins once you submit your sitemap and establish a measurement cadence. Use a Domain property for full coverage of subdomains and protocols, then add a URL‑prefix property for precise path‑level filters if you need granular diagnostics.
Submit the Yoast sitemap index and verify that child sitemaps resolve correctly. For medium and large sites, consider segmenting content types into separate sitemaps, then monitor them individually. If a particular content type shows high “Discovered, currently not indexed,” reassess quality, internal linking, and crawlability for that segment.
In the Performance report, create saved filters using regex to compare page templates. Group results by page path patterns like ^/blog/ or ^/docs/ to reveal which templates underperform on CTR or average position. Track cannibalization by switching the dimension to Pages and checking which URLs compete on the same query. If multiple similar URLs split impressions, consolidate with internal linking and canonical signals refined in Yoast.
Use URL Inspection as your canonical truth source. Ensure the inspected URL’s canonical matches your Yoast canonical setting, then view the rendered HTML to confirm meta tags output as intended. If Google selects a different canonical, tighten internal linking, reduce near‑duplicates, and confirm only one strong URL variant appears in your sitemaps.
In Enhancements, watch for structured data errors tied to your schema selections. If you add an FAQ block on a guide and see Rich Results impressions rise, annotate the date and compare CTR pre‑ and post‑change. Reinforce wins with additional rich‑eligible sections where they make sense. For live debugging of rich data, the Rich Results Test from Google is faster than waiting on recrawls, and the Yoast schema defaults give a solid base.
For hands‑on walk‑throughs, the Complete Yoast SEO Tutorial for Beginners 2025 on YouTube and the detailed Yoast setup video provide complementary instruction. Use them as visual checkpoints while you run your own experiments.
Evolving the On‑Page Workflow: From Green Bullets to Search Intent Signals
Green bullets validate the basics. To push beyond, map search intent and subtopics before you open the editor. For a complex guide, plan the entity connections, related questions, and internal link targets in advance. Use Yoast to set the primary keyphrase, then evaluate related phrases that inform H2s and H3s. Your goal is comprehensive topical coverage, not repetition. Mark cornerstone pieces and direct internal links from supporting articles to those hubs, then revisit the internal linking suggestions to reinforce the structure as your library grows.
For schema, select the right type per post. Articles can be NewsArticle or BlogPosting depending on format; evergreen documentation might be best expressed as TechArticle even if you keep Yoast’s defaults and enrich with proper blocks. If you operate an ecommerce store, confirm Product schema coherence with your product plugin and avoid duplicate schema output from overlapping tools. Validate often in the Rich Results Test and confirm GSC Enhancements show clean, interpretable graphs.

Industry‑Specific Configurations and What Usually Breaks
Ecommerce
Index product and curated category pages; noindex filtered facets, pagination beyond page one where thin, and internal search URLs
Ensure each product has unique images and descriptions; align Product schema attributes with actual content
Use internal linking from editorial content to top revenue categories to concentrate equity
B2B SaaS
Canonicalize versioned docs; surface a single latest‑version guide as canonical
Noindex changelogs unless they have clear search demand; if indexed, cluster by version and add a hub page
Establish entity clarity for the brand and key personnel through About and Team pages with consistent profile links
Local and multi‑location
Build location pages with unique NAP data and localized copy; consider LocalBusiness schema via compatible plugins or fields
Avoid indexing thin city/service combinations; consolidate to robust service hubs and link to store pages
Ensure your entity home matches your chosen representation in Yoast, then align with your Google Business Profile
Publishers
Noindex low‑value tag archives and stale date archives
Standardize author pages if authors are a differentiator, including bio, expertise, and external profile links
Validate Article schema and test headline and image ratios for optimal display
For foundational learners who still want a structured path alongside this yoast seo training, you can pair these steps with a search engine optimization tutorial for beginners from the Yoast academy or compare guidance from the Semrush overview and the Kinsta walkthrough to triangulate best practices.
A Measurement Framework Aligned to Real Outcomes
Use a weekly and monthly rhythm that ties GSC data to content actions:
Weekly
- Inspect newly published URLs, confirm indexation, and verify expected canonical
- Monitor the Performance report for new queries, CTR anomalies, and early rich result impressions
- Review Coverage for unexpected noindex flags or blocked resources; fix quickly if caused by template changes
Monthly
- Template‑level audit by regex filter groups to see which content types underperform
- Internal linking review: add links from traffic winners to cornerstone pages that need lift
- Sitemap health check by child sitemap; prune sitemaps of decommissioned sections
Track KPIs that reflect business impact:
- Net indexed pages vs. published pages for each content type
- Share of top‑10 keywords per template
- CTR change for URLs where titles and meta descriptions were rewritten
- Rich result impressions and CTR for FAQ, How‑to, or Product
- Crawl status distribution, especially Discovered vs. Crawled vs. Indexed
When data suggests content or architecture changes, annotate the date in GSC and your change log. Re‑check two weeks later for directional movement and decide whether to roll forward, iterate, or revert.
If you are mapping a comprehensive learning arc, complement this with a technical seo course approach and project work. Two companion pieces that fit neatly here are choosing the right SEO training online and a free SEO training roadmap for structured practice. For content execution, fold in an SEO copywriting training curriculum to build drafts that satisfy intent and pass editorial standards. For advanced workflows, explore machine learning in SEO to scale keyword clustering, internal linking discovery, and anomaly detection.
For step‑by‑step refreshers and alternative takes, the YouTube beginner tutorials, the Semrush guide, and the Kinsta deep dive remain useful reference points within a broader set of seo tutorials that you can adapt to your stack and governance model.
Conclusion
Ultimately, you built a search-ready WordPress site with precise configuration: titles and meta, indexing rules, schema, sitemaps, and sane permissions—giving crawlers a single, coherent source of truth. This search engine optimization tutorial for beginners replaced guesswork with a practical, repeatable system you can apply on every page.
Your on-page workflow now runs on intent: focused keyphrases, compelling titles and slugs, concise descriptions, clear structure, and purposeful internal linking. Schema decisions for articles, FAQs, and how-tos, validated through rich result checks, lock in clarity for search engines and open the door to enhanced listings.
Monitoring is no longer optional; it’s the engine of improvement. Treat Google Search Console training as your feedback loop—verify, submit sitemaps, review Coverage and Enhancements, inspect URLs, and translate findings into precise adjustments in Yoast and content.
Discipline sustains momentum. Keep one SEO plugin, maintain clean permalinks, noindex thin archives, resolve duplicates with canonicals, and prevent title/meta conflicts. Pair this with image compression and performance hygiene to compound gains.
In conclusion, the path forward is clear: complete the one-time setup, optimize your next three posts with the per-post checklist, and schedule recurring GSC reviews. Expand your edge with focused seo tutorials and, when ready, a technical seo course to scale your results. With yoast seo training as your foundation, publish, measure, and iterate now—the compounding gains start the moment you act.
Frequently Asked Questions
Yoast’s SEO analysis checks how well your page targets a focus keyphrase (title, H1, slug, first paragraph, links, and ALT text), while the Readability analysis evaluates sentence length, paragraph structure, passive voice, and transition words. Prioritize aligning content with search intent first, then use both analyses to refine clarity and relevance. Green bullets are guides, not absolute rules—focus on producing a page that answers the query thoroughly and naturally.
Create a full backup and, ideally, use a staging site. In Yoast, use the built-in Import tool to bring over titles, meta descriptions, and redirects from plugins like Rank Math or All in One SEO. Deactivate the old plugin to prevent conflicts, then crawl key templates (home, posts, categories) to confirm titles and canonicals match expectations. For small sites, plan 30–60 minutes; larger sites may need a few hours and spot checks in Google Search Console.
Use noindex when pages should exist but not appear in search (e.g., thin tag archives, internal thank-you pages). They can remain in the sitemap so Google sees them and respects the directive. Use exclude (remove from sitemap) for content you don’t want to highlight at all (e.g., test CPTs, staging remnants). Keep important navigational pages indexed; overusing either can hurt crawl efficiency and topical coverage. Re-check the result in URL Inspection after changes.
Start with Performance to spot which pages or queries lost clicks, then use URL Inspection to check live status, canonical selection, and last crawl date. Review Coverage and Enhancements for sudden spikes in errors (noindex, 404, schema issues). Confirm your sitemap is processed and includes the affected URLs. Map the timing of drops to recent changes (templates, redirects, noindex toggles). Expect 48–72 hours for many fixes to be reflected, and longer for rankings to stabilize.
Yoast outputs core schema by default (WebPage/Article plus Organization/Person). Choose specific types per post when needed: FAQ for Q&A sections, HowTo for step-by-step guides, and Product/Event/LocalBusiness when relevant via compatible plugins or CPTs. Use the Rich Results test and the Enhancements report in Search Console for validation, and fix conflicts like duplicate schema from themes or other plugins. Correct schema increases eligibility for rich results and can improve CTR.
Review titles and descriptions monthly for key pages and quarterly sitewide. Prioritize pages with high impressions but low CTR relative to their average position. Triggers for rewrites include CTR underperforming compared to similar pages, outdated offers or dates, and titles that don’t match search intent. Use consistent title templates for branding, but tailor high-value URLs manually. Expect incremental CTR lifts of 2–10% when you sharpen relevance and value props.
No. Yoast focuses on metadata, sitemaps, and content optimization—not performance. Core Web Vitals require caching, image compression, critical CSS, and server/CDN improvements. While better titles and schema can boost visibility, slow pages can cap rankings and harm UX. Run site speed audits, fix largest elements (images, scripts), and retest. Treat performance work as a parallel stream to your Yoast SEO training.
Enable Breadcrumbs in Yoast, then integrate them via your theme. Many themes offer a breadcrumb location in their settings; if not, a developer can add the Yoast breadcrumb function to a header or single template. Place breadcrumbs above the title or below the header for best navigation and internal linking clarity. After implementation, confirm the breadcrumb trail is consistent and doesn’t duplicate H1s.
Frequent issues include “Submitted URL not in sitemap,” redirected or 404 URLs, and blocklisted URLs (robots). Fix by ensuring only indexable content types are enabled in Yoast’s Sitemap settings, removing redirects and errors from the sitemap, and aligning noindex choices with Search Appearance. Re-submit the sitemap and request indexing for fixed URLs via URL Inspection. Most sitemap-related warnings clear within 1–3 days after corrections.
The free plugin covers titles/meta, sitemaps, schema, and per-page robots controls—enough for a search engine optimization tutorial for beginners. Yoast Premium adds a Redirect Manager, internal linking suggestions, multiple focus keyphrases, and advanced content insights. If you frequently change URLs or do migrations, built-in redirects are a strong reason to upgrade. Otherwise, you can combine Yoast free with a dedicated redirect plugin and still follow this technical SEO course approach effectively.
Indexing and snippet updates can appear in 24–72 hours, but meaningful ranking and traffic gains typically take 4–12 weeks, depending on crawl frequency, competition, and content quality. Publishing new, intent-matched content, improving internal links to cornerstone pages, and routine google search console training reviews accelerate progress. Keep iterating—steady improvements compound faster than one-time changes from isolated SEO tutorials.